Types of Plastics and Their Functions
Plastics have often been portrayed as non-recyclable and a source of environmental problems, but in this article, we aim to highlight why plastics play a vital role in today’s world, particularly in the injection molding machine industry. Understanding the different types of plastics is essential for selecting the most suitable material for various manufacturing processes, especially when using injection molding machines.
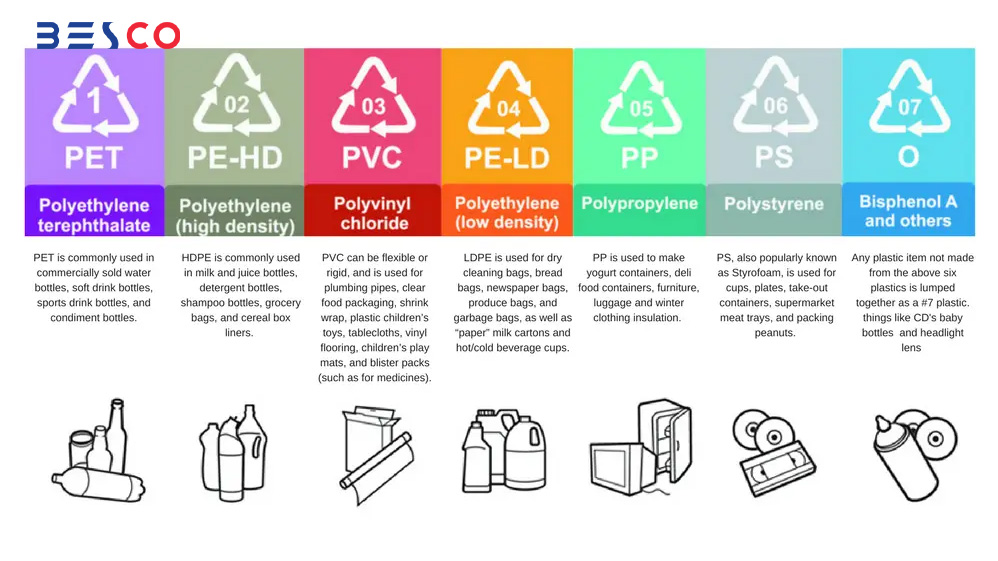
The Evolution of Plastics
Not all plastics are created equal. Although plastics have been unfairly vilified, the truth is that only a few types are dangerous, and even these are improving year by year. So, how do we identify the right plastic for our use, and how can we determine if it is safe?
1. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
PET is one of the most commonly used plastics, especially for single-use water bottles. You may have heard that PET is a dangerous plastic, and indeed, it is one of the types that has been associated with risks. Although it is widely used for storing food and beverages due to its ability to prevent oxygen from entering or leaving the container, it was once believed to contain carcinogenic substances linked to cancer. Heat and PET do not mix well.
2. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE is a thick, dense plastic commonly used for milk cartons, shampoo bottles, and grocery bags. This plastic is highly stable, recyclable, and generally considered safe and useful.
3. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC can be very rigid, and it is used in a variety of applications, from toys to blood bags. Unfortunately, PVC is one of the more hazardous plastics, as it releases harmful chemicals like BPA during both production and recycling, posing risks to both human health and the environment.
4. Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is another versatile plastic known for its high resistance to heat and safety in various applications. You can find it in items like disposable diapers, car parts, and even heat vests. It is a durable and commonly used material.
5. Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene, or PS, is another plastic that has its drawbacks. When exposed to heat, it releases toxic chemicals. Additionally, recycling PS is particularly difficult, and there is minimal effort made to recycle this material.
6. Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
LDPE is typically very thin and flexible, often used for plastic wraps or cable coverings. While recycling LDPE can be more challenging, it is considered safe for the environment.
7. Polyethylene (PE)
PE comes in various forms, including both high-density (HDPE) and low-density (LDPE) polyethylene. Known for its resistance to chemicals and moisture, as well as its insulating properties, PE is flexible and commonly used in packaging materials, pipes, electrical cable insulation, and containers.
8. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is a strong, impact-resistant plastic with good surface hardness and appearance. It is easy to machine and has excellent mechanical strength. ABS is used in a wide range of applications, including automotive parts, consumer electronics housings, and even Lego bricks.
9. Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is extremely durable, impact-resistant, and has good optical clarity. It also has heat resistance and can be easily molded. Common uses include eyewear lenses, safety helmets, bulletproof glass, and electronic components.
10. Polyamide (Nylon) (PA)
Nylon is known for its high tensile strength, excellent wear resistance, and good chemical resistance. It is also flexible and can withstand high temperatures. Nylon is widely used in textiles (such as socks and ropes), automotive parts (like gears and bearings), and industrial applications (machine parts).
11. Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane is a versatile plastic with varying properties, ranging from hard to flexible. It has good resistance to wear and chemicals and is commonly used as foam. It can be found in furniture (foam cushions), coatings, adhesives, and elastomers for various industrial applications.
12. Polylactic Acid (PLA)
PLA is a biodegradable plastic made from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. It has good optical clarity and is resistant to moisture and fat. PLA is used in biodegradable packaging, disposable containers, medical implants, and even 3D printing.
By understanding these different types of plastics and their characteristics, we can make more informed decisions about which materials are best suited to meet our needs while minimizing harm to the environment and human health.
